| New Threat Detection Added | 2 - FortiWLM Unauthenticated SQL Injection (CVE-2023-34991) and Operation Crimson Palace - XiebroC2 CnC |
| New Threat Protections | 178 |
Weekly Detected Threats
The following threats were added to Crystal Eye XDR this week:
Threat name: | FortiWLM Unauthenticated SQL Injection (CVE-2023-34991) | ||||||||||||||||||
Fortinet's Wireless LAN Manager (FortiWLM) has been found to contain several critical security vulnerabilities that could allow remote attackers to compromise the system fully. These vulnerabilities include unauthenticated command injection (CVE-2023-34993), unauthenticated SQL injection (CVE-2023-34991), and unauthenticated arbitrary file read (CVE-2023-42783). Exploiting these flaws could lead to unauthorised command execution, database manipulation, and access to sensitive files, respectively. FortiWLM is commonly deployed in large enterprise environments, making these vulnerabilities particularly concerning. Fortinet has released patches to address these issues, and it is strongly recommended that affected organisations apply these updates promptly. | |||||||||||||||||||
Threat Protected: | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||
Rule Set Type: |
| ||||||||||||||||||
Class Type: | Attempted-admin | ||||||||||||||||||
Kill Chain: |
| ||||||||||||||||||
Threat name: | Operation Crimson Palace - XiebroC2 CnC | ||||||||||||||||||
Operation Crimson Palace is a sophisticated cyberespionage campaign attributed to Chinese state-sponsored actors, targeting government agencies and public service organisations in Southeast Asia. The campaign employs advanced tactics, including DLL sideloading, to deploy custom malware such as "TattleTale," a previously undocumented keylogger. The attackers have demonstrated adaptability by shifting to open-source tools and varying their command-and-control (C2) channels to evade detection. Notably, compromised infrastructure within the same verticals has been leveraged to stage malware and relay C2 communications, indicating a strategic approach to blending into the targeted environments. | |||||||||||||||||||
Threat Protected: | 5 | ||||||||||||||||||
Rule Set Type: |
| ||||||||||||||||||
Class Type: | Trojan-activity | ||||||||||||||||||
Kill Chain: |
| ||||||||||||||||||
Known exploited vulnerabilities (Week 3 - December 2024)
For more information, please visit the Red Piranha Forum:
https://forum.redpiranha.net/t/known-exploited-vulnerabilities-catalog-3rd-week-of-december-2024/533
Vulnerability | CVSS | Description | |
CVE-2024-35250 | 7.8 (High) | Microsoft Windows Kernel-Mode Driver Untrusted Pointer Dereference Vulnerability | |
CVE-2024-20767 | 7.4 (High) | Adobe ColdFusion Improper Access Control Vulnerability | |
CVE-2024-55956 | 9.8 (Critical) | Cleo Multiple Products Unauthenticated File Upload Vulnerability | |
CVE-2021-40407 | 9.8 (Critical) | Reolink RLC-410W IP Camera OS Command Injection Vulnerability | |
CVE-2019-11001 | 7.2 (High) | Reolink Multiple IP Cameras OS Command Injection Vulnerability | |
CVE-2022-23227 | 9.8 (Critical) | NUUO NVRmini 2 Devices Missing Authentication Vulnerability | |
CVE-2018-14933 | 9.8 (Critical) | NUUO NVRmini Devices OS Command Injection Vulnerability | |
CVE-2024-12356 | 9.8 (Critical) | BeyondTrust Privileged Remote Access (PRA) and Remote Support (RS) Command Injection Vulnerability |
Updated Malware Signatures (Week 3 - December 2024)
Threat | Description | |
Lumma Stealer | A type of malware classified as an information stealer. Its primary purpose is to steal sensitive information from infected systems, including but not limited to credentials, financial information, browser data, and potentially other personal or confidential information. | |
Remcos | Remcos functions as a remote access trojan (RAT), granting unauthorised individuals the ability to issue commands on the compromised host, record keystrokes, engage with the host's webcam, and take snapshots. Typically, this malicious software is distributed through Microsoft Office documents containing macros, which are often attached to malicious emails. |
| Ransomware Report | |
The Red Piranha Team conducts ongoing surveillance of the dark web and other channels to identify global organisations impacted by ransomware attacks. In the past week, our monitoring revealed multiple ransomware incidents across diverse threat groups, underscoring the persistent and widespread nature of these cyber risks. Presented below is a detailed breakdown of ransomware group activities during this period. | |
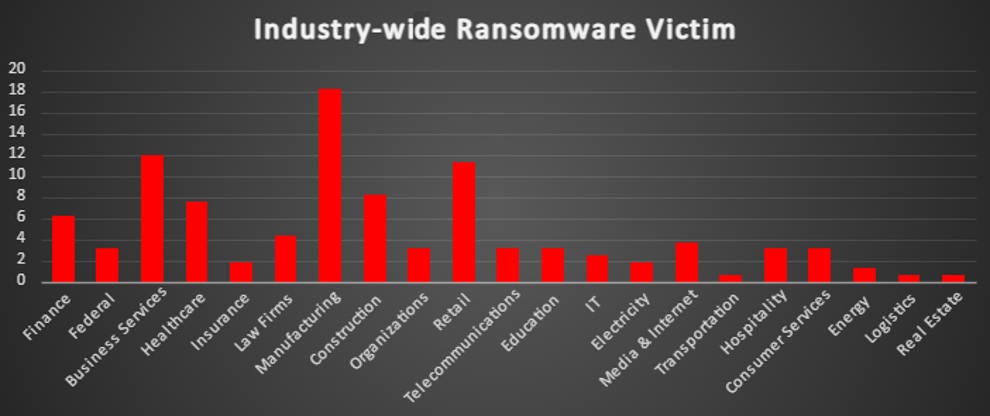
| Name of Ransomware Group | Overall %age of total attack coverage |
Funksec | 14.47% |
Bianlian | 3.14% |
8.81% | |
El Dorado | 3.77% |
Killsec3 | 4.4% |
Cicada3301 | 1.26% |
Handala | 0.63% |
Akira | 9.43% |
Team Underground | 0.63% |
7.55% | |
Eraleign (APT73) | 1.89% |
Argonauts Group | 0.63% |
Dragonforce | 2.52% |
Leaked Data | 1.26% |
Lynx | 1.89% |
Qilin | 3.77% |
Kairos | 1.26% |
4.4% | |
Stormous | 0.63% |
Everest | 3.77% |
Interlock | 1.89% |
Hunters | 3.77% |
Nitrogen | 1.89% |
3AM | 0.63% |
Brain Cipher | 1.26% |
Bluebox | 1.89% |
0.63% | |
Cactus | 0.63% |
Nullbulge | 0.63% |
Blackbasta | 3.14% |
1.26% | |
Money Message | 0.63% |
2.52% | |
Cloak | 1.26% |
Abyss-data | 0.63% |
0.63% | |
Space Bears | 0.63% |
Fog Ransomware Group
Fog Ransomware emerged in April 2024, targeting both Windows and Linux endpoints. It operates as a multi-pronged extortion operation, utilising a TOR-based Data Leak Site (DLS) to publicly list victims and host exfiltrated data from those who refuse to meet ransom demands.
This ransomware is part of the modern ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) ecosystem, with customisable payloads tailored to disrupt operations in targeted environments.
Detailed TTPs
Initial Access and Foothold Establishment:
- Primary Initial Access Methods:
- Exploitation of known vulnerabilities in public-facing systems.
- Use of compromised credentials purchased from Initial Access Brokers (IABs).
- Post-Access Lateral Movement: Systematic traversal across network endpoints using valid credentials.
Cross-Platform Payloads:
- Windows Variant: Focuses on shadow copy deletion, service termination, and extensive configuration capabilities.
- Linux Variant: Targets virtual environments (e.g., VMSD and VMDK files) and employs tailored commands for environment disruption.
Fog Ransomware supports multiple command-line parameters. These include:
Parameter Description
File Encryption Behavior:
Windows Configuration: JSON-based configuration enabling:
- Custom encrypted file extensions.
- Ransom note filename configuration.
- Service and process termination lists.
- RSA public key embedding for encryption operations.
Readme.txt
Fog Data Leak Site (DLS):
First Observed: July 2024
Ransom Note:
- File Name: readme.txt
- Content: Instructions for victim communication via a TOR-based victim portal.
FOG SAMPLES: MD5
Mutex Name
FOG RANSOMWARE HOSTNAMES
How to Mitigate Fog Ransomware
2. Implement Strong Authentication Controls:
- Enforce strong password policies.
- Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) for all remote and administrative access.
3. Network Hardening:
- Restrict RDP and SSH Access:
- Use VPNs for secure access.
- Enforce MFA on remote access portals.
- Implement network segmentation to prevent lateral movement.
4. System and Software Updates:
- Regularly apply security patches and updates to operating systems, software, and firmware.
- Disable unnecessary services and protocols.
5. Backup and Disaster Recovery:
- Perform frequent, encrypted backups of critical systems and data.
- Store backups in offline, air-gapped environments.
- Regularly test data recovery processes.
6. Endpoint Protection:
- Enable real-time monitoring and alerting for suspicious activities.
7. Network Monitoring and Logging:
- Enable network anomaly detection tools.
- Monitor log files for early indicators of compromise (IOCs).
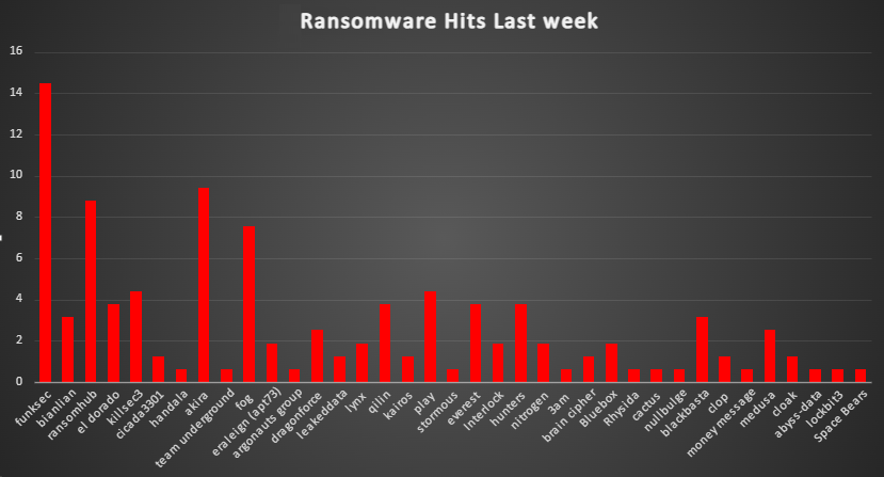
Ransomware Victims Worldwide
A recent ransomware analysis reveals a striking 55.97% of global incidents targeted the United States, making it the hardest-hit country by far. Trailing behind, Canada experienced 5.66% of attacks, while Australia, France, Brazil, and India each reported 3.14%.
Other significantly affected countries include Germany at 2.52%, followed by the United Kingdom at 1.89%. Nations such as China, Italy, Poland, Sweden, and Indonesia each reported 1.26% of the total attacks.
Meanwhile, a diverse group of nations, including Mexico, Netherlands, Nigeria, Mongolia, Thailand, Israel, Saudi Arabia, Poland, Greece, Ukraine, Belgium, Ecuador, Sri Lanka, Hong Kong, Jamaica, Vietnam, Spain, Argentina, Egypt, and Botswana, each saw a limited impact, representing just 0.63% of the total incidents.
This analysis underscores the global and persistent nature of ransomware threats, with North America bearing the brunt of the attacks, followed by Europe and parts of Asia. These numbers emphasise the critical need for enhanced cybersecurity measures across all regions to combat the ever-evolving ransomware threat landscape.
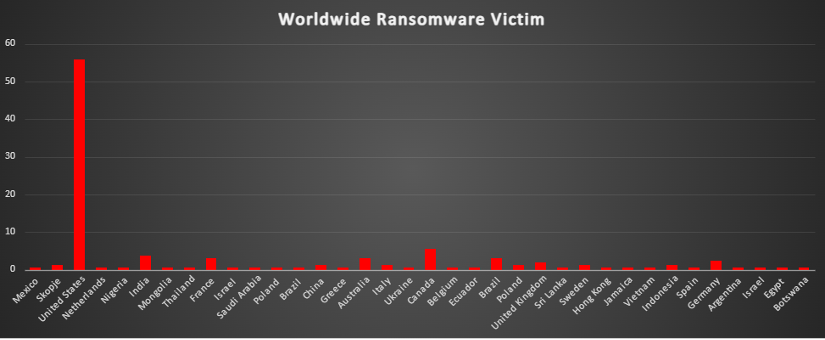
Ransomware Victims Industry-wide
Ransomware attacks continue to disrupt industries across the board, with the Manufacturing sector emerging as the hardest hit, accounting for a significant 18.24% of all incidents. Trailing closely behind, the Business Services sector faced 11.95%, while Retail reported 11.32% of attacks, highlighting their vulnerability to cyber threats.
The Healthcare sector follows with 7.55%, emphasising its critical exposure to ransomware disruptions. Construction also experienced notable impacts, representing 8.18% of total incidents. Meanwhile, Finance recorded 6.29%, reflecting its continued attractiveness as a target due to high-value data.
Sectors such as Law Firms (4.4%), Media & Internet (3.77%), Federal (3.14%), Telecommunications (3.14%), Education (3.14%), Hospitality (3.14%), Organisations (3.14%), and Consumer Services (3.14%) have all faced mid-level impacts from ransomware operations.
Smaller, yet significant, shares of attacks were observed in IT (2.52%), Insurance (1.89%), Electricity (1.89%), and Energy (1.26%), indicating ongoing risks in infrastructure-critical sectors.
Lower incidence rates were reported in Transportation (0.63%), Logistics (0.63%), and Real Estate (0.63%), though no industry can claim immunity from ransomware threats.
These numbers paint a clear picture: ransomware attacks are indiscriminate, targeting critical infrastructure, public services, and corporate entities alike. This broad distribution across industries highlights the urgent need for proactive cybersecurity strategies, tailored risk assessments, and incident response plans to mitigate the escalating threat of ransomware worldwide