| New Threat Detection Added | 2 |
| • SVCStealer • GorillaBot |
|
| New Threat Protections | 191 |
Weekly Detected Threats
The following threats were added to Crystal Eye this week:
|
Threat name:
|
SVCStealer | ||||||||||||||||||
|
SVCStealer is classified as an information stealer that was first observed in January 2025. It is a C++ based malware that’s designed to harvest sensitive data including browser credentials, cryptocurrency wallets, as well as personal files, and system information. It’s often spread through phishing emails and embedded in malicious executables and has the capability to download additional payloads.
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
Threat Protected:
|
03 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
Rule Set Type:
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Class Type:
|
Malware | ||||||||||||||||||
|
Kill Chain:
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Threat name:
|
GorillaBot | ||||||||||||||||||
|
GorillaBot is a Mirai-based trojan that’s primarily used to carry out DDoS attacks. It was first observed in September 2024 and is used by threat actors in a DDoS-for-hire service.
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
Threat Protected:
|
03 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
Rule Set Type:
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Class Type:
|
Malware | ||||||||||||||||||
|
Kill Chain:
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (Week 2 - June 2025)
For more information, please visit the Red Piranha Forum:
https://forum.redpiranha.net/t/known-exploited-vulnerabilities-catalog-3rd-week-of-june-2025/568
|
Vulnerability
|
CVSS
|
Description |
|
CVE-2025-33053
|
8.8 (High)
|
Web Distributed Authoring and Versioning (WebDAV) contains a vulnerability that can allow an unauthenticated remote attacker to execute code on a system upon user interaction with a specially crafted URL.
|
|
CVE-2025-24016
|
9.9 (Critical)
|
Wazuh contains a deserialisation vulnerability that can allow a remote authenticated attacker to execute code on a system by sending a specially crafted API request. This vulnerability affects versions 4.4.0 through to 4.9.0 and was fixed in version 4.9.1.
|
|
CVE-2024-42009
|
9.3 (Critical)
|
RoundCube Webmail contains a cross-site scripting vulnerability that can allow a remote attacker to execute arbitrary code via an email that can result in an attacker gaining the ability to read and send emails.
|
|
CVE-2025-32433
|
10 (Critical)
|
Erlang Erlang/OTP SSH server contains a vulnerability that can allow an unauthenticated remote attacker to execute arbitrary commands on a system without authentication.
|
Updated Malware Signatures (Week 2 - June 2025)
|
Threat
|
Description
|
|
|
zgRAT
|
A Remote Access Trojan (RAT) used in cyberattacks that provides attackers remote access to a machine. Commonly spread in malware loaders and through phishing emails.
|
| Ransomware Report | |
|
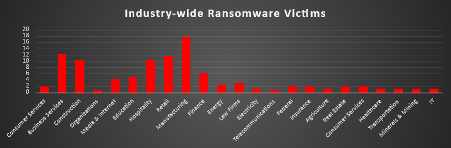
The Red Piranha Team conducts ongoing surveillance of the dark web and other channels to identify global organisations impacted by ransomware attacks. In the past week, our monitoring revealed multiple ransomware incidents across diverse threat groups, underscoring the persistent and widespread nature of these cyber risks. Presented below is a detailed breakdown of ransomware group activities during this period. Ransomware Hits Last Week Qilin leads the threat landscape this week, responsible for 17.79% of reported ransomware incidents. Its dominance points to a sustained and highly active campaign, likely supported by a robust affiliate network and evolving tooling. NightSpire follows closely with 15.95%, continuing to rise as a formidable mid-tier actor with broad international reach and increasing operational tempo. Akira holds 14.72%, maintaining a strong presence across sectors with a reputation for targeting both service providers and infrastructure-heavy organisations. Warlock accounts for 11.66%, a notable uptick that may suggest targeted regional campaigns or new affiliate operations. Global and TeamXXX follow with 6.13% and 4.29%, respectively, both indicating growing activity that warrants further monitoring. WorldLeaks and SafePay registered 3.68% and 3.07%, with Apos also at 3.07%, all showing consistent low-to-mid-level campaigns across varied geographies. A cluster of actors including Medusa, Inc Ransom, Direwolf, and Interlock (each around 1.84%) remain active, frequently relying on double extortion and opportunistic access. Other groups such as Play, Everest, Lynx, Rhysida, Devman, Arkana Security, Stormous, RansomHouse, Walocker, Space Bears, Sarcoma, Anubis, DataCarry, Fsociety, and Frag each accounted for 0.61%–1.23%. These actors illustrate the fragmented nature of the ransomware ecosystem, where dozens of smaller players contribute to the global attack volume and complicate detection and attribution efforts. |
NightSpire Ransomware
NightSpire surfaced in March 2025 and has already posted more than 60 organisations to its Tor leak portal. Last week, the gang published 18 new victims, primarily in manufacturing, finance, hospitality and healthcare. The campaign leans on CVE-2024-55591 (FortiOS SSL-VPN) for foothold, executes a statically linked Go loader, and exfiltrates data with TOR-proxied MEGAcmd before encryption. Files are renamed “*.nspire” and OneDrive content is also locked, amplifying pressure on victims.
Technical Analysis
-
Unpatched FortiOS SSL-VPN (CVE-2024-55591) exploited for root shell.
-
Low-volume phishing delivering Go loaders with macro-less VBA stagers.
-
Opportunistic RDP brute force against cloud hosts in the education sector.
-
Go binary spawns under conhost.exe; schedules task “OneDrive Update Service” at log-on.
-
Registry Run-key HKCU\...\ExplorerUpdate for user-level persistence.
-
Harvests creds with Mimikatz, redeploys via PsExec/WMI.
-
Invokes Everything.exe to enumerate SMB/NAS shares.
-
TOR beacons to nspire*.onion and new node a2ly...nqd.onion.
-
Bulk data staged through MEGAcmd over port 443.
-
AES-256 per-file; RSA-4096 master; “*.nspire” extension; uniform readme.txt.
|
Tactic
|
Technique
|
Evidence
|
|
Initial Access
|
T1190 Exploit Public-Facing App
|
CVE-2024-55591
|
|
Execution
|
T1059.001 PowerShell
|
Loader stager
|
|
Persistence
|
T1053.005 Scheduled Task
|
OneDrive Update Service
|
|
Priv Esc
|
T1068 Exploitation for Priv-Esc
|
FortiOS root shell
|
|
Defence Evasion
|
T1218 Signed-Binary Proxy
|
WinSCP / MEGAcmd
|
|
Discovery
|
T1046 Network Service Discovery
|
Everything.exe scans
|
|
Lateral Move
|
T1021 Remote Services
|
PsExec pivots
|
|
C2
|
T1090.003 Multi-Hop Proxy
|
TOR .onion nodes
|
|
Exfiltration
|
T1567.002 Exfil to Cloud
|
MEGAcmd uploads
|
|
Impact
|
T1486 Data Encryption
|
“.nspire” files
|
IOCs
- File Hashes
- C2 / Leak-Site Domains
- Attacker Contact Channels
- ProtonMail night.spire.team@proton.me
- OnionMail nightspireteam.receiver@onionmail.org
- Gmail night.spire.team@gmail.com
- OnionMail (alt) night.spire.team@onionmail.org
- ProtonMail (alt) nightspireteam.receiver@proton.me
- Telegram https://t.me/night_spire_team (@night_spire_team)
- qTox ID: 3B61CFD6E12D789A439816E1DE08CFDA58D76EB0B26585AA34CDA617C41D5943CDD15DB0B7E6
- Host & Filesystem Artefacts
- File extension: .nspire
- Ransom note: readme.txt
- LOLBins / tools: Everything.exe, WinSCP.com, MEGAcmd
- Scheduled Task: OneDrive Update Service
- Registry Run-key: HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run\ExplorerUpdate
Detection & Response Recommendations
-
Patch FortiOS to 7.4.6 or apply FG-IR-24-55591 interim fix.
-
Monitor for TOR SNI strings resolving to the above *.onion domains and block outbound connections.
-
Alert on the creation of Everything.exe in non-standard paths followed by share enumeration (ANY.RUN).
-
Inline IDPS rules – The built-in intrusion-protection engine in CE 5.0 can detect FortiOS exploit traffic and automatically quarantine hosts (here).
-
Threat-Hunt Dashboard – SOC teams gain one-click pivots from anomalous TOR beacons to full packet captures via the CE 5.0 Threat Hunt view (here).
-
Embedded SIEM & Incident-Response SLA – By forwarding host logs into the Incident & Event Services module and pre-defining SLA tiers, organisations cut mean-time-to-respond when NightSpire indicators trip (here).
-
Best-Practice Hardening – CE 5.0’s configuration baseline enables strict application control that blocks unsigned Go binaries—closing the door on the NightSpire loader (here).
-
Enforce MFA on all VPN/RDP access and restrict RDP to jump hosts.
-
Maintain 3-2-1 backups with at least one copy offline to thwart OneDrive encryption.
-
Develop playbooks that combine Sigma/YARA detections for “.nspire” artefacts with automated host isolation.
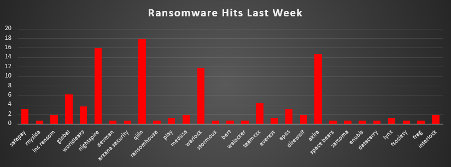
Ransomware Victims Worldwide
The United States remains the most targeted country this week, accounting for a dominant 42.94% of all reported ransomware victims. This overwhelming share highlights its expansive digital footprint, high-value targets, and continuous exploitation by both known and emerging ransomware operators.
Australia ranks second with 7.36%, underscoring increased activity in the Asia-Pacific region. Its reliance on cloud infrastructure and interconnected digital services makes it an appealing target.
Spain follows with 5.52%, reflecting persistent threat actor focus on Western Europe—particularly sectors such as retail, logistics, and manufacturing.
Canada and the United Kingdom also faced notable activity, recording 4.91% and 4.29%, respectively. These economies continue to attract ransomware due to their technological maturity and volume of critical business services.
Italy and Portugal posted 3.07% and 2.45%, while countries like India, Norway, and the United Arab Emirates each saw 1.84% of incidents, showing widespread distribution across regions including Europe, the Middle East, and South Asia.
A broad swath of countries—including Mexico, Brazil, Singapore, Venezuela, Austria, Turkey, Peru, South Africa, Germany, Poland, and France—each experienced 1.23% of the attacks. These mid-tier figures suggest that attackers are actively probing both mature and emerging economies.
Meanwhile, countries such as New Zealand, Czech Republic, Egypt, Kuwait, South Korea, Kenya, Denmark, Croatia, Chile, Ireland, Thailand, Greece, Netherlands, Switzerland, Mauritius, and Ukraine each registered 0.61% of ransomware incidents. This long-tail distribution illustrates the global reach of modern ransomware groups—no nation is off-limits, and even those with smaller digital footprints are frequently caught in opportunistic campaigns.
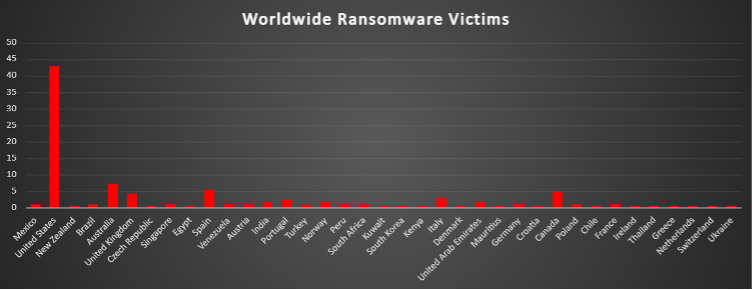
Industry-wide Ransomware Victims
Manufacturing continues to be the most targeted sector, accounting for 17.79% of all ransomware incidents this week. Its complex supply chains and high reliance on uptime make it a prime target for disruption-based extortion.
Business Services follow at 12.27%, with attackers focusing on consulting firms, third-party vendors, and logistics providers that act as intermediaries for critical infrastructure and enterprise clients.
Retail and Construction reports 11.66% and 10.43%, respectively. Both sectors are frequent victims due to high transaction volumes, dispersed operations, and often under-resourced cybersecurity practices.
Hospitality mirrors Construction with 10.43%, driven by its data-rich environments and frequent handling of personal and financial information, making it attractive for both encryption and data theft.
The Finance sector saw 6.13% of incidents—consistent with ransomware operators targeting financial institutions for both monetary gain and reputational leverage.
Education registered 4.91%, highlighting continued pressure on academic institutions, which often have wide attack surfaces and limited security budgets. Media & Internet followed with 4.29%, showing that information platforms remain valuable targets for disruption and disinformation.
Other notable sectors include:
- Law Firms: 3.07% - due to the sensitivity of legal data.
- Energy: 2.45% - critical infrastructure exposure.
- Healthcare, Agriculture, Transportation, Minerals & Mining, Electricity, IT: 1.23% each - emphasising a broad attack spectrum across essential services.
- Consumer Services, Federal, Insurance, Real Estate: 1.84% each - often part of larger extortion campaigns.
- Telecommunications and Organisations: 0.61% each - showing even niche or isolated sectors are not immune.