| New Threat Detection Added | 2 (Parrot TDS and SquidLoader Malware) |
| New Threat Protections | 119 |
Weekly Detected Threats
The following threats were added to Crystal Eye XDR this week:
Threat name: | Parrot TDS | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
A new cyber threat called Parrot TDS has infected over 16,500 websites, including university and government sites. This system redirects users to malicious campaigns like FakeUpdate, which tricks them into downloading remote access tools. Unlike prior threats, Parrot TDS targets a wider range of poorly secured websites, putting millions at risk. Researchers identified a surge in activity in February 2022 and estimate Parrot TDS has been active since October 2021. They protected over 600,000 users from visiting infected sites in a month, with Brazil, India, and the US being the most impacted. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Threat Protected: | 03 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Rule Set Type: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Class Type: | Trojan-activity | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Kill Chain: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Threat name: | SquidLoader Malware | ||||||||||||||||||
Researchers have identified a new, evasive malware loader named SquidLoader, which targets Chinese organisations through phishing campaigns. SquidLoader utilises various techniques to evade detection and deploys a Cobalt Strike payload. LevelBlue Labs suspects this actor has been active for over two years with a focus on Chinese targets. While the current campaign targets a specific region, the techniques used by SquidLoader could be adopted by other malware creators in future attacks, posing a threat to a wider audience. | |||||||||||||||||||
Threat Protected: | 01 | ||||||||||||||||||
Rule Set Type: |
| ||||||||||||||||||
Class Type: | Trojan-activity | ||||||||||||||||||
Kill Chain: |
| ||||||||||||||||||
Known exploited vulnerabilities (Week 3 - June 2024)
Threat | CVSS | Description | |
CVE-2024-31982 | 10.0 (Critical) | XWiki Remote Code Execution Vulnerability | |
CVE-2024-28999 | 8.1 (High) | SolarWinds Race Condition Vulnerability | |
CVE-2024-34470 | Ongoing Analysis | HSC Mailinspector Path Traversal Vulnerability |
For more information, please visit the Red Piranha Forum:
https://forum.redpiranha.net/t/known-exploited-vulnerabilities-catalog-3rd-week-of-june-2024/480
Updated Malware Signatures (Week 3 - June 2024)
Threat | Description | |
Nanocore | The Nanocore trojan, built on the .NET framework, has been the subject of multiple source code leaks, resulting in its widespread accessibility. Like other remote access trojans (RATs), Nanocore empowers malicious actors with complete system control, enabling activities such as video and audio recording, password theft, file downloads, and keystroke logging. | |
Remcos | Remcos functions as a remote access trojan (RAT), granting unauthorised individuals the ability to issue commands on the compromised host, record keystrokes, engage with the host's webcam, and take snapshots. Typically, this malicious software is distributed through Microsoft Office documents containing macros, which are often attached to malicious emails. | |
Lumma Stealer | A type of malware classified as an information stealer. Its primary purpose is to steal sensitive information from infected systems, including but not limited to credentials, financial information, browser data, and potentially other personal or confidential information. |
| Ransomware Report | |
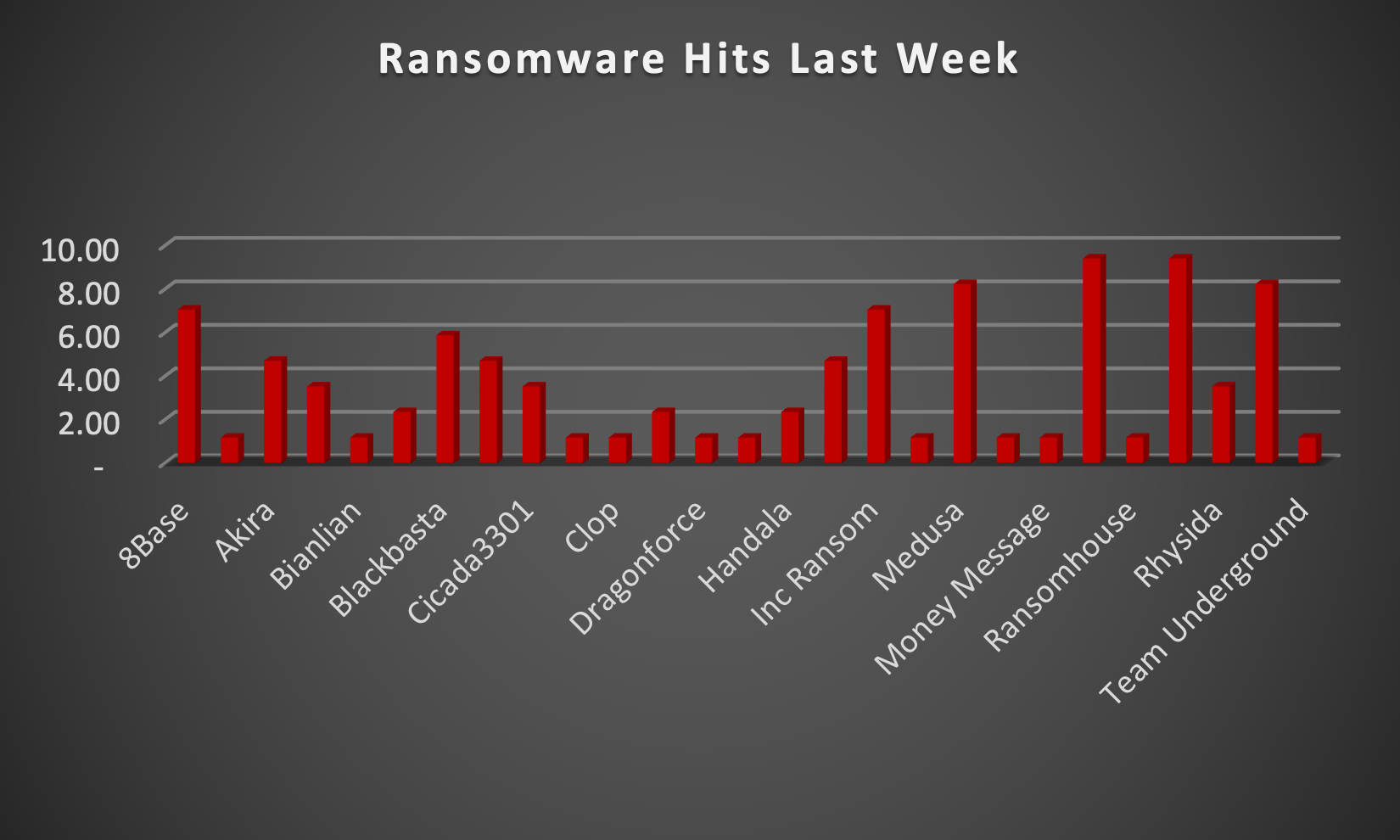
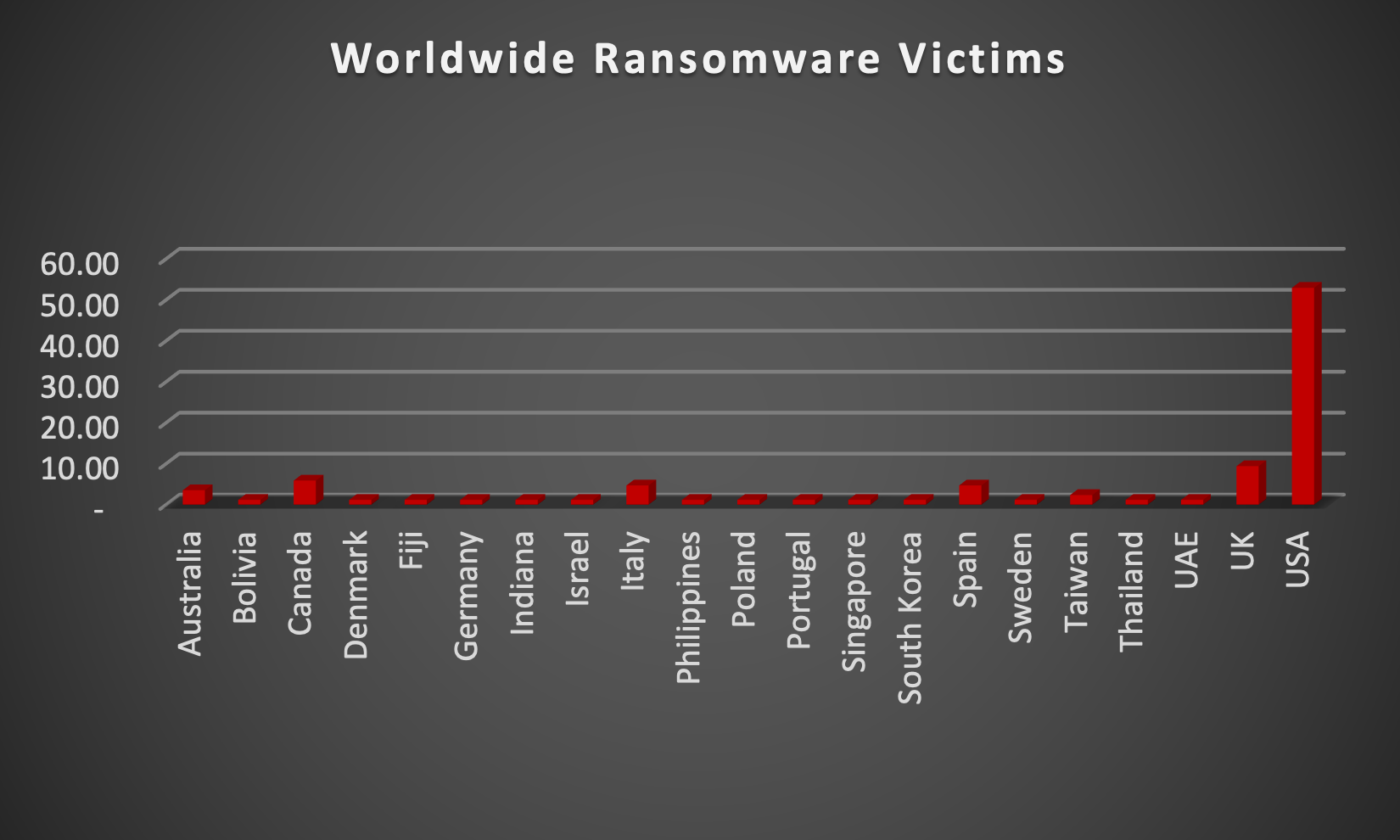
The Red Piranha Team actively collects information on organisations globally affected by ransomware attacks from various sources, including the Dark Web. In the past week alone, our team uncovered new ransomware victims and updates on previous victims across 18 industries spanning 21 countries. This underscores the widespread and indiscriminate impact of ransomware attacks, emphasising their potential to affect organisations of varying sizes and sectors worldwide. Qilin and Ransomhub ransomware groups stand out as the most prolific, having updated a significant number of victims (9%) each distributed across multiple countries. In comparison, Medusa and Space Bears ransomware updated 8% victims each, in the past week. The following list provides the victim counts in percentages for these ransomware groups and a selection of others. | |
| Name of Ransomware Group | Percentage of new Victims last week |
8Base | 7.06% |
Abyss-Data | 1.18% |
Akira | 4.71% |
Arcus Media | 3.53% |
Bianlian | 1.18% |
Black Suit | 2.35% |
Blackbasta | 5.88% |
Cactus | 4.71% |
Cicada3301 | 3.53% |
Cloak | 1.18% |
1.18% | |
Darkvault | 2.35% |
Dragonforce | 1.18% |
Eraleign (Apt73) | 1.18% |
Handala | 2.35% |
Hunters | 4.71% |
Inc Ransom | 7.06% |
1.18% | |
Medusa | 8.24% |
Metaencryptor | 1.18% |
Money Message | 1.18% |
Qilin | 9.41% |
Ransomhouse | 1.18% |
Ransomhub | 9.41% |
Rhysida | 3.53% |
Space Bears | 8.24% |
Team Underground | 1.18% |
Qilin Ransomware
Emerging in July 2022, Qilin ransomware, also known as Agenda, has established itself as a formidable threat actor in the cybercrime landscape. This ruthless malware operates using a double extortion model, crippling victims by encrypting their data and threatening to leak it on the dark web if ransom demands aren't met. While the exact origins of Qilin remain unclear, security researchers believe it might be linked to a cybercriminal group operating as as-a-service. This group offers its ransomware tools and expertise to affiliates who launch attacks against various targets.
Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures (TTPs):
Qilin isn't a one-trick pony. It possesses a diverse arsenal of tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) to infiltrate and compromise systems. Here's a glimpse into its malicious toolkit:
- Phishing Attacks: Deceptive emails designed to trick users into clicking malicious links or downloading infected attachments are a common entry point. These emails may appear to be from trusted sources such as delivery companies, financial institutions, or even colleagues.
- Exploiting Unpatched Vulnerabilities: Qilin actively seeks out unpatched vulnerabilities in software and operating systems to gain unauthorised access to networks. This underscores the importance of keeping all software and systems updated with the latest security patches.
- Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) Exploitation: Like other ransomware strains, Qilin can exploit weaknesses in RDP configurations to gain access to a system. RDP allows remote access to a computer, and misconfigured settings can create a vulnerability for attackers.
- Brute-Force Attacks: In some instances, Qilin may attempt to gain access through brute-force attacks, where it systematically tries different combinations of usernames and passwords until it cracks the login credentials. This highlights the importance of using strong passwords and enabling multi-factor authentication (MFA) where possible.
- Living-off-the-Land Techniques: Like many malware strains, Qilin can utilise legitimate system administration tools for malicious purposes. This makes detection more challenging as these tools may appear as normal system activity.
Read all about Living-off-the-land techniques and how ATPs use them. - Data Exfiltration: Before encryption, Qilin often exfiltrates sensitive data like financial records, personal information, and intellectual property. This stolen data serves as additional leverage in extortion attempts, putting pressure on victims to pay the ransom.
- Strong Encryption: The malware utilises robust encryption algorithms to render files inaccessible. Decrypting them without the attacker's key is extremely difficult, if not impossible. This effectively cripples a victim's operations until a decision is made.
A Global Reach with Focused Targets:
Qilin ransomware demonstrates a lack of geographical bias, targeting victims worldwide. Here are some examples of its reach and the damage it has caused:
- Critical Infrastructure: Security researchers have observed that Qilin targets critical infrastructure sectors like power grids and transportation systems. A successful attack on such infrastructure could have devastating consequences.
- Healthcare Organisations: Hospitals and other healthcare providers have also fallen victim to Qilin attacks. The disruption caused by encrypted medical records and operational systems can severely impact patient care.
- Educational Institutions: Schools and universities haven't been spared either. Data breaches involving student information or disruption of educational services can have serious consequences.
Leak Site: Qilin ransomware maintains a leak site on the dark web where they threaten to publish stolen data if the ransom is not paid.
Ransom Note: The Qilin ransomware has many different ransom notes for every victim. One of the ransom notes is given below:
The emergence of Qilin ransomware underscores the ever-evolving threat landscape of cybercrime. Its use of readily available tools combined with its focus on double extortion tactics, highlights the need for organisations to prioritise robust cybersecurity measures. Here are some crucial steps organisations can take to mitigate the risk of Qilin ransomware and similar threats:
- Regular Backups: Maintain secure, offline backups of critical data to facilitate recovery in case of a ransomware attack.
- Patch Management: Implement a rigorous patch management system to ensure all software and operating systems are updated with the latest security patches.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Enable MFA for all user accounts wherever possible. MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring a second verification factor beyond just a username and password.
- Security Awareness Training: Educate employees on identifying phishing attempts and other social engineering tactics used by attackers. Regular training can significantly reduce the risk of human error leading to breaches.
- Endpoint Security Solutions: Deploy endpoint security solutions that can detect and prevent malware infections at the device level. These solutions can act as a first line of defence against Qilin and other malware threats.
Kill Chain:
Tactic | Technique ID | Technique Name |
Initial Access | T1078 T1566 T1190 | Valid Accounts Phishing Exploit Public-Facing Application |
Execution | T1059 T1053 | Command and Scripting Interpreter Scheduled Task/Job |
Persistence | T1136 | Boot or Logon Initialization Scripts |
Privilege Escalation | T1068 T1548 | Exploitation of Vulnerabilities Abuse Elevation Control Mechanism |
Defence Evasion | T1562 T1027 T1070 | Impair Defences Obfuscated Files or Information Indicator Removal |
Credential Access | T1555 T1003 | Credentials from Password Stores OS Credential Dumping |
Discovery | T1049 T1083 | System Network Connections Discovery File and Directory Discovery |
Lateral Movement | T1072 T1570 | Software Deployment Tools Lateral Tool Transfer |
Collection | T1119 | Automated Collection |
Exfiltration | T1567 | Exfiltration Over Web Service |
Command-and-Control | T1219 T1090 | Remote Access Software Proxy |
Impact | T1486 T1485 T1490 T1561.001 | Data Encrypted for Impact Data Destruction Inhibit System Recovery Data Wipe |
Indicators of Compromise (IOCs)
Indicators | Indicator Type | Description |
http://ozsxj4hwxub7gio347ac7tyqqozvfioty37skqilzo2oqfs4cw2mgtyd.onion/ http://24kckepr3tdbcomkimbov5nqv2alos6vmrmlxdr76lfmkgegukubctyd.onion http://wlh3dpptx2gt7nsxcor37a3kiyaiy6qwhdv7o6nl6iuniu5ycze5ydid.onion/blog http://kbsqoivihgdmwczmxkbovk7ss2dcynitwhhfu5yw725dboqo5kthfaad.onion/ https://wikileaksv2.com | URLs (Onion) | Leak Site |
e90bdaaf5f9ca900133b699f18e4062562148169b29cb4eb37a0577388c22527 55e070a86b3ef2488d0e58f945f432aca494bfe65c9c4363d739649225efbbd1 37546b811e369547c8bd631fa4399730d3bdaff635e744d83632b74f44f56cf6 555964b2fed3cced4c75a383dd4b3cf02776dae224f4848dcc03510b1de4dbf4 fd7cbadcfca84b38380cf57898d0de2adcdfb9c3d64d17f886e8c5903e416039 76f860a0e238231c2ac262901ce447e83d840e16fca52018293c6cf611a6807e | Hash | File |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
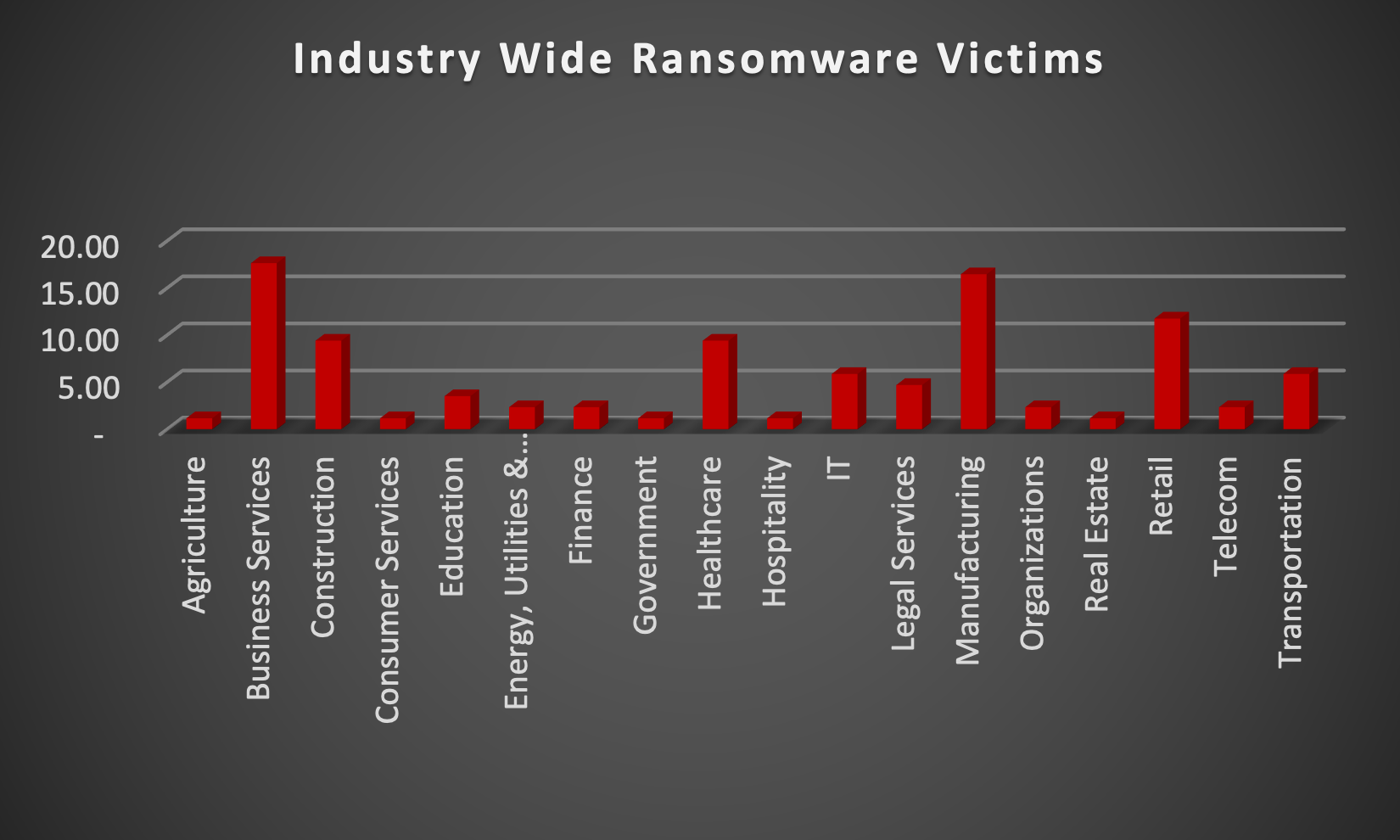
Upon further investigation, it has been identified that ransomware has left its mark on 18 different industries worldwide. Notably, Manufacturing bore the brunt of the attacks in the past week, accounting for 16% of victims. There are a few key reasons why the manufacturing sector is a prime target for ransomware groups:
- High Disruption Potential: Manufacturing relies heavily on interconnected systems and just-in-time production. A ransomware attack can grind operations to a halt, causing significant financial losses due to production delays and lost revenue. This pressure to get back online quickly can make manufacturers more willing to pay the ransom.
- Vulnerable Legacy Systems: Many manufacturers use legacy control systems (OT) that haven't been updated for security. These older systems often lack robust security features, making them easier targets for attackers to exploit.
- Limited Cybersecurity Investment: Traditionally, cybersecurity might not have been a top priority for some manufacturers compared to production efficiency. This lack of investment in security awareness training and robust security protocols leaves them exposed.
- Valuable Data: Manufacturing facilities often hold valuable intellectual property (IP) and trade secrets. Ransomware groups may not only disrupt operations but also threaten to leak this sensitive data if the ransom isn't paid.
- Success Breeds Success: The high payout potential from past attacks on manufacturers incentivises ransomware groups to continue targeting them.
The table below delineates the most recent ransomware victims, organised by industry, shedding light on the sectors grappling with the significant impact of these cyber threats.
Name of the affected Industry | Victims Count (%) |
Agriculture | 1.18% |
Business Services | 17.65% |
Construction | 9.41% |
Consumer Services | 1.18% |
Education | 3.53% |
Energy, Utilities & Waste Treatment | 2.35% |
Finance | 2.35% |
Government | 1.18% |
Healthcare | 9.41% |
Hospitality | 1.18% |
IT | 5.88% |
Legal Services | 4.71% |
Manufacturing | 16.47% |
Organisations | 2.35% |
Real Estate | 1.18% |
Retail | 11.76% |
Telecom | 2.35% |
Transportation | 5.88% |