
| New Threat Detection Added | 4 (Rodmacer Stealer, VersaMem Malware, Moonpeak RAT and Cthulu Stealer) |
| New Threat Protections | 236 |
Weekly Detected Threats
The following threats were added to Crystal Eye XDR this week:
Threat name: | Rodmacer Stealer | ||||||||||||||||||
Rodmacer Stealer is a potent information-stealing malware that has emerged as a significant threat in the cyber landscape. This malware targets a wide range of sensitive data, including login credentials, credit card information, cryptocurrency wallet details, and personal files. Rodmacer's advanced capabilities, such as keylogging, screen capturing, and file exfiltration, make it a formidable tool for cybercriminals. Often distributed through phishing emails or malicious downloads, Rodmacer poses a significant risk to both individuals and organisations. Effective cybersecurity measures, including vigilant email practices, strong password management, and regular software updates, are essential to protect against this and other malware threats. | |||||||||||||||||||
Threat Protected: | 01 | ||||||||||||||||||
Rule Set Type: |
| ||||||||||||||||||
Class Type: | Trojan-activity | ||||||||||||||||||
Kill Chain: |
| ||||||||||||||||||
Threat name: | VersaMem Malware | ||||||||||||||||||
VersaMem is a sophisticated malware family known for its advanced evasion techniques and persistence. This threat actor, believed to be state-sponsored, has been active since at least 2021, targeting government, military, and critical infrastructure sectors. VersaMem's capabilities include data exfiltration, remote code execution, and system control. Its modular architecture allows for customisation, making it a versatile tool for malicious activities. The malware's ability to evade detection, combined with its affiliation with a well-resourced threat actor, makes VersaMem a significant threat to organisations worldwide. | |||||||||||||||||||
Threat Protected: | 03 | ||||||||||||||||||
Rule Set Type: |
| ||||||||||||||||||
Class Type: | Trojan-activity | ||||||||||||||||||
Kill Chain: |
| ||||||||||||||||||
Threat name: | Moonpeak RAT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Moonpeak RAT is a sophisticated Remote Access Trojan (RAT) that has emerged as a significant threat in the cyber landscape. This malware offers attackers extensive control over compromised systems, enabling them to steal data, execute commands, and establish persistent backdoors. Moonpeak's modular architecture allows for customisation, making it a versatile tool for cybercriminals. The malware's ability to evade detection, combined with its affiliation with a well-resourced threat actor, makes Moonpeak a significant concern for organisations worldwide. Effective cybersecurity measures, including vigilant email practices, strong password management, and regular software updates, are essential to protect against this and other malware threats. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Threat Protected: | 08 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Rule Set Type: |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Class Type: | Trojan-activity | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Kill Chain: |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Threat name: | Cthulu Stealer | ||||||||||||||||||
Cthulu Stealer is a potent information-stealing malware that has emerged as a significant threat in the cyber landscape. This malware targets a wide range of sensitive data, including login credentials, credit card information, cryptocurrency wallet details, and personal files. Cthulu Stealer's advanced capabilities, such as keylogging, screen capturing, and file exfiltration, make it a formidable tool for cybercriminals. Often distributed through phishing emails or malicious downloads, Cthulu Stealer poses a significant risk to both individuals and organisations. Effective cybersecurity measures, including vigilant email practices, strong password management, and regular software updates, are essential to protect against this and other malware threats. | |||||||||||||||||||
Threat Protected: | 02 | ||||||||||||||||||
Rule Set Type: |
| ||||||||||||||||||
Class Type: | Trojan-activity | ||||||||||||||||||
Kill Chain: |
| ||||||||||||||||||
Known exploited vulnerabilities (Week 5 - September 2024)
Threat | CVSS | Description | |
CVE-2024-7971 | 8.8 (High) | Google Chromium V8 Type Confusion Vulnerability | |
CVE-2024-38856 | 9.8 (Critical) | Apache OFBiz Incorrect Authorisation Vulnerability | |
CVE-2024-7965 | 8.8 (High) | Google Chromium V8 Inappropriate Implementation Vulnerability |
For more information, please visit the Red Piranha Forum:
https://forum.redpiranha.net/t/known-exploited-vulnerabilities-catalog-5th-week-of-august-2024/501
Updated Malware Signatures (Week 5 - September 2024)
Threat | Description | |
Glupteba | A malware dropper that is designed to download additional malware on an infected machine. | |
Lumma Stealer | A type of malware classified as an information stealer. Its primary purpose is to steal sensitive information from infected systems, including but not limited to credentials, financial information, browser data, and potentially other personal or confidential information. | |
BlankGrabber Stealer | BlankGrabber stealer malware is a type of malicious software designed to steal sensitive information from an infected system. This information can include login credentials, passwords, browser cookies, stored credit card information, and other personal data. The malware typically operates by extracting this data from web browsers, applications, and system files where such information is commonly stored. |
| Ransomware Report | |
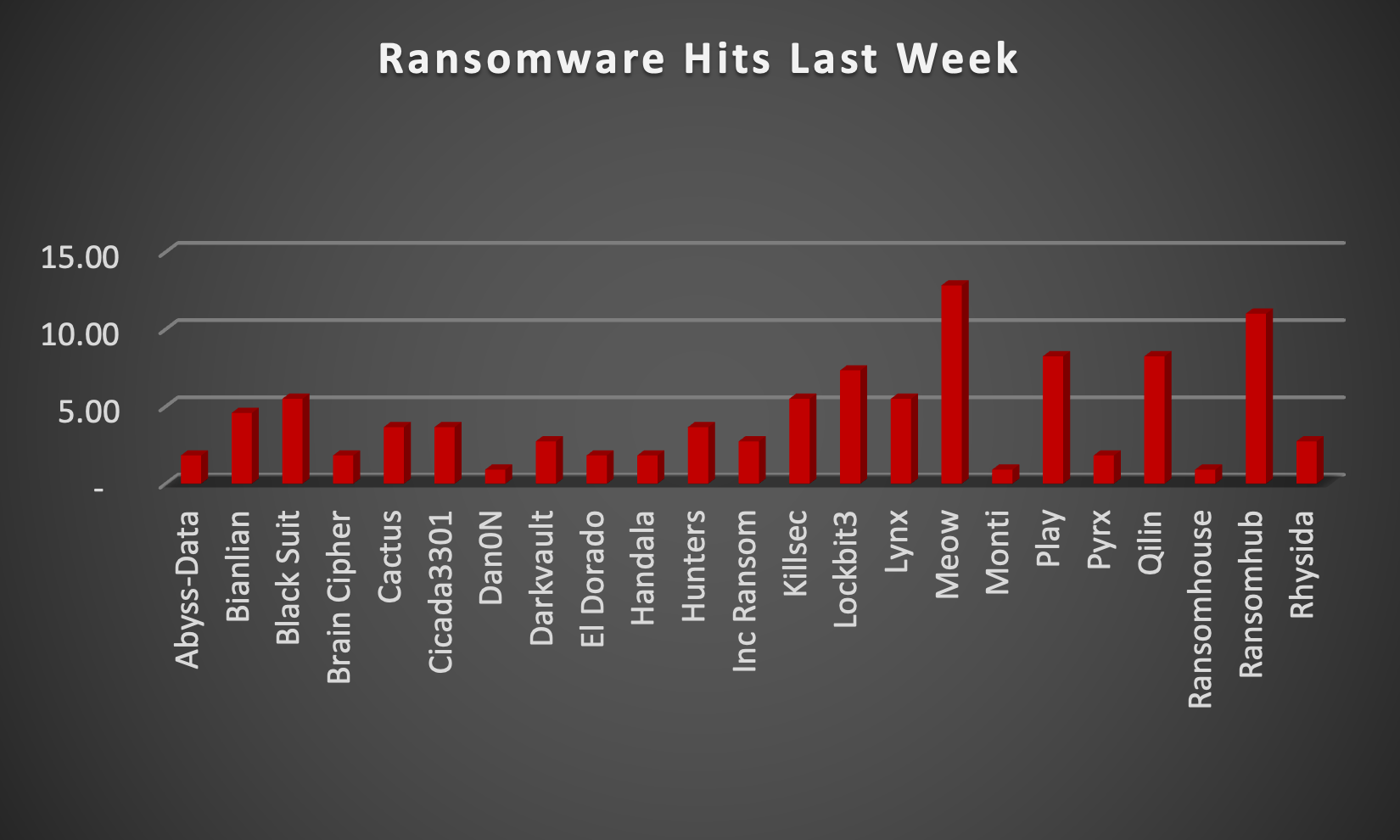
The Red Piranha Team actively collects information on organisations globally affected by ransomware attacks from various sources, including the Dark Web. In the past week alone, our team uncovered new ransomware victims and updates on previous victims across 22 different industries spanning 27 countries. This underscores the widespread and indiscriminate impact of ransomware attacks, emphasising their potential to affect organisations of varying sizes and sectors worldwide. Meow ransomware group stands out as the most prolific, having updated many victims (13%) distributed across multiple countries. In comparison, RansomHub ransomware updated 11% of victims, in the past week. The following list provides the victim counts in percentages for these ransomware groups and a selection of others. | |
| Name of Ransomware Group | Percentage of new Victims last week |
Abyss-Data | 1.83% |
Bianlian | 4.59% |
BlackSuit | 5.50% |
Brain Cipher | 1.83% |
Cactus | 3.67% |
Cicada3301 | 3.67% |
Dan0N | 0.92% |
Darkvault | 2.75% |
El Dorado | 1.83% |
Handala | 1.83% |
Hunters | 3.67% |
Inc Ransom | 2.75% |
Killsec | 5.50% |
7.34% | |
Lynx | 5.50% |
Meow | 12.84% |
Monti | 0.92% |
8.26% | |
Pyrx | 1.83% |
Qilin | 8.26% |
RansomHouse | 0.92% |
11.01% | |
Rhysida | 2.75% |
BlackSuit Ransomware
BlackSuit ransomware, a formidable threat in the cybercrime landscape, emerged as a rebranded version of the notorious Royal ransomware group in early 2023. This sophisticated malware employs a double extortion tactic, encrypting victims' data and threatening to leak it on the dark web if ransom demands aren't met. BlackSuit's origins can be traced back to the Conti cybercrime syndicate, highlighting its deep roots in the criminal underworld.
TTPs:
BlackSuit possesses a diverse arsenal of tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) to infiltrate and compromise systems.
- Phishing Attacks: Deceptive emails designed to trick users into clicking malicious links or downloading infected attachments are a common entry point.
- Exploiting Vulnerabilities: BlackSuit actively seeks out unpatched vulnerabilities in software and operating systems to gain unauthorised access to networks.
- Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) Exploitation: Misconfigured RDP settings can create vulnerabilities that BlackSuit can exploit to gain access to systems.
- Supply Chain Attacks: Targeting vulnerabilities in software suppliers or third-party vendors can provide a way for BlackSuit to infiltrate a wider network of victims.
Data Leak Site: BlackSuit ransomware maintains a data leak site on the dark web where they list victims who haven't paid the ransom. This serves as a public shaming tactic and adds pressure on compromised organisations.
Figure 2: Screenshot of Leak Site used by BlackSuit Ransomware
Ransom Note
BlackSuit ransomware, a notorious cyber threat, employs a deceptive tactic in its ransom notes. Rather than demanding a ransom outright, it presents itself as a "README.BlackSuit.txt" This facade aims to manipulate victims into believing they have a chance to recover their encrypted data for a fee.
However, this is a deceptive ploy. Once a victim pays the ransom, there's no guarantee that their data will be decrypted. In many cases, victims are left with no option but to rebuild their systems and data from backups.
Figure 3: Screenshot of Ransom Note used by BlackSuit Ransomware
A Global Reach with Focused Targets
BlackSuit has demonstrated a global reach, targeting victims across various industries and geographies.
- Healthcare Organisations: Hospitals and healthcare providers have been frequent targets due to the sensitive nature of patient data and the potential disruption to critical services.
- Manufacturing Disruptions: Manufacturing companies worldwide have experienced data breaches and operational disruptions due to BlackSuit attacks.
- Financial Institutions: The financial sector has also been targeted, with banks and credit unions facing potential data breaches and economic losses.
Kill Chain
Tactic | Technique ID | Technique Name |
Execution | T1059.001 T1569.002 T1059.003 | PowerShell Service Execution Windows Command Shell |
Persistence | T1547.001 | Registry Run Keys / Startup Folder |
Privilege Escalation | T1548 | Abuse Elevation Control Mechanism |
Defence Evasion | T1112 T1055 | Modify Registry Process Injection |
Credential Access | T1558.004 T1558.003 T103.001 | AS-REP Roasting Kerberoasting LSASS Memory |
Discovery | T1069.002 T1482 T1018 T1518.001 T1518 T1082 | Domain Groups Domain Trust Discovery Remote System Discovery Security Software Discovery Software Discovery System Information Discovery |
Collection | T1560 | Archive Collected Data |
Command-and-Control | T1090 T1071.001 | Proxy Web Protocol |
Impact | T1486 T1490 | Data Encrypted for Impact Inhibit System Recovery |
Indicators | Indicator Type | Description |
hxxp://weg7sdx54bevnvulapqu6bpzwztryeflq3s23tegbmnhkbpqz637f2yd.onion | URLs (Onion) | Leak Site |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
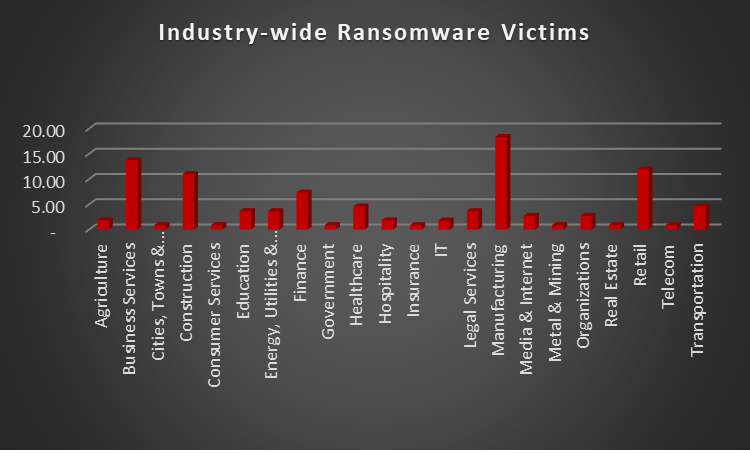
Upon further investigation, it has been identified that ransomware has left its mark on 22 different industries worldwide. Notably, Manufacturing bore the brunt of the attacks in the past week, accounting for 18% of victims each. There are a few key reasons why the manufacturing sector is a prime target for ransomware groups:
- High Disruption Potential: Manufacturing relies heavily on interconnected systems and just-in-time production. A ransomware attack can grind operations to a halt, causing significant financial losses due to production delays and lost revenue. This pressure to get back online quickly can make manufacturers more willing to pay the ransom.
- Vulnerable Legacy Systems: Many manufacturers use legacy control systems (OT) that haven't been updated for security. These older systems often lack robust security features, making them easier targets for attackers to exploit.
- Limited Cybersecurity Investment: Traditionally, cybersecurity might not have been a top priority for some manufacturers compared to production efficiency. This lack of investment in security awareness training and robust security protocols leaves them exposed.
- Valuable Data: Manufacturing facilities often hold valuable intellectual property (IP) and trade secrets. Ransomware groups may not only disrupt operations but also threaten to leak this sensitive data if the ransom isn't paid.
- Success Breeds Success: The high payout potential from past attacks on manufacturers incentivises ransomware groups to continue targeting them.
Name of the affected Industry | Victims Count (%) |
Agriculture | 1.83% |
Business Services | 13.76% |
Cities, Towns & Municipalities | 0.92% |
Construction | 11.01% |
Consumer Services | 0.92% |
Education | 3.67% |
Energy, Utilities & Waste Treatment | 3.67% |
Finance | 7.34% |
Government | 0.92% |
Healthcare | 4.59% |
Hospitality | 1.83% |
Insurance | 0.92% |
IT | 1.83% |
Legal Services | 3.67% |
Manufacturing | 18.35% |
Media & Internet | 2.75% |
Metal & Mining | 0.92% |
Organisations | 2.75% |
Real Estate | 0.92% |
Retail | 11.93% |
Telecom | 0.92% |
Transportation | 4.59% |
According to recent data, the manufacturing industry was the most heavily targeted by ransomware groups in 2024, followed by business services and hospitality.
Here are some crucial steps organisations can take to mitigate the risk of ransomware and similar threats:
- Third-Party Risk Management: Implement a comprehensive third-party risk management program to assess and monitor the security posture of vendors and suppliers.
- Supply Chain Visibility: Maintain visibility into your supply chain to identify potential risks and vulnerabilities.
- Regular Backups: Maintain secure, offline backups of critical data to facilitate recovery in case of a ransomware attack.
- Patch Management: Implement a rigorous patch management system to ensure all software and operating systems are updated with the latest security patches.
- Security Awareness Training: Educate employees on identifying phishing attempts and other social engineering tactics used by attackers. Regular training can significantly reduce the risk of human error leading to breaches.
- Endpoint Security Solutions: Deploy endpoint security solutions that can detect and prevent malware infections at the device level. These solutions can act as a first line of defence against BlackSuit and other malware threats.
- Network Segmentation: Segmenting your network can limit the lateral movement of ransomware, potentially preventing it from spreading throughout your entire infrastructure.
- Incident Response Planning: Develop and regularly test an incident response plan to effectively respond to a ransomware attack and minimise damage. Having a plan in place ensures a more coordinated and efficient response during a crisis.
